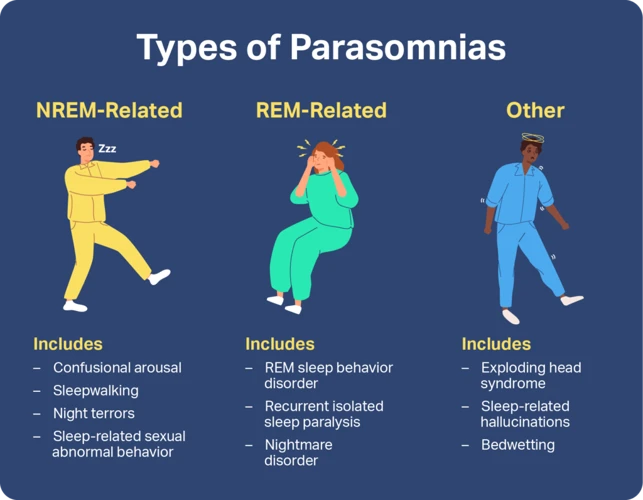
Contents
- Sleep Paralysis Overview
- Causes of Sleep Paralysis
- Symptoms of Sleep Paralysis
- Diagnosing Sleep Paralysis
- Treating Sleep Paralysis
- Managing Sleep Paralysis and Related Disorders
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is sleep paralysis and why does it occur?
- What are the neurological factors that can lead to sleep paralysis?
- Can sleep deprivation and disrupted sleep patterns cause sleep paralysis?
- Are mental health and stress related to sleep paralysis?
- What are the main symptoms of sleep paralysis?
- How is sleep paralysis diagnosed?
- What are some treatments for sleep paralysis?
- Can sleep paralysis be managed and prevented?
- Is sleep paralysis dangerous?
- Can sleep paralysis be linked to other sleep disorders?
- References
Sleep Paralysis Overview
Sleep paralysis is a phenomenon that involves a temporary inability to move or speak when falling asleep or waking up. During sleep paralysis, a person may feel conscious and aware of their surroundings, but they cannot move their body or respond to external stimuli. This can be a scary and unsettling experience, and it can happen to anyone at least once in their life.
Sleep paralysis mainly occurs during two phases of sleep: the transition from wakefulness to sleep (hypnagogic or predormital sleep paralysis) or from sleep to wakefulness (hyperagogic or postdormital sleep paralysis). During these transitions, the body undergoes natural changes to allow for sleep or waking, respectively. However, sleep paralysis can occur when these changes are interrupted, leading to the body being paralyzed while the mind remains conscious.
Sleep paralysis is not considered to be a serious medical condition, but it can be indicative of underlying sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea or narcolepsy. Additionally, some people may experience sleep paralysis as a symptom of anxiety or depression, as well as other mental health conditions.
Although sleep paralysis is a relatively common experience, it can still be distressing for those who experience it. It can be accompanied by vivid hallucinations, feelings of intense fear, and difficulty breathing. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of sleep paralysis is crucial for those who experience it or know someone who does.
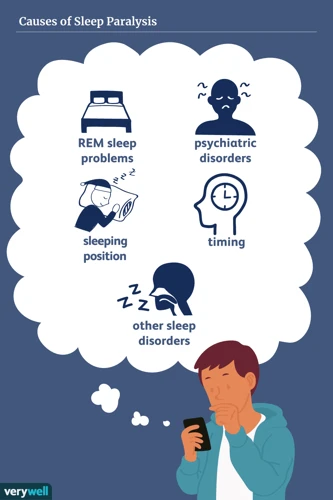
Causes of Sleep Paralysis

As unsettling as sleep paralysis can be, the causes behind the condition are not entirely clear. Scientists have identified several potential factors that may contribute to this phenomenon. Some of these factors are related to neurological or physical issues, while others are associated with sleep disruption and mental health conditions. Let’s delve deeper into these factors to better understand the potential causes of sleep paralysis.
Neurological and Physical Factors
There are various neurological and physical factors that can potentially lead to sleep paralysis. These factors include genetics, narcolepsy, and disrupted circadian rhythms . Narcolepsy is a sleeping disorder that affects the brain’s ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles. It occurs due to a lack of hypocretin, a neuropeptide in the brain that regulates wakefulness. Individuals with narcolepsy have a higher prevalence of sleep paralysis.
Sleep paralysis has also been observed in individuals with disrupted circadian rhythms, such as those with shift work disorder or jet lag. These disturbances disrupt the natural pattern of sleep and wakefulness, leading to excessive sleepiness during the day and difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep at night.
Another factor that contributes to the occurrence of sleep paralysis is neurological conditions like migraines, and strokes. Migraines can cause visual and sensory disturbances which can potentially trigger sleep paralysis. Strokes can also affect the brain’s ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles, leading to an increased risk of sleep paralysis.
Additionally, certain physical conditions like obstructive sleep apnea and hypothyroidism can also cause sleep paralysis. Obstructive sleep apnea is a sleep disorder that can cause a person to stop breathing while they are asleep. Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland produces insufficient amounts of hormones, leading to a slower metabolism and fatigue.
It is important to note that these factors do not necessarily cause sleep paralysis in all individuals who have them. However, they can increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. Understanding these factors can help individuals take steps towards preventing sleep paralysis and getting the necessary treatment if they experience it.
Sleep Deprivation and Disruptive Sleep Patterns
Sleep Deprivation and Disruptive Sleep Patterns
Sleep deprivation and disruptive sleep patterns are among the most common causes of sleep paralysis. Lack of sleep or poor sleep quality can significantly impact brain function and the ability to enter and exit different stages of sleep.
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Irregular Sleep Schedule | Going to bed and waking up at different times every day can disrupt your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, leading to difficulty falling asleep and staying asleep. |
| Narcolepsy | A condition that causes excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden, uncontrollable episodes of falling asleep. |
| Sleep Apnea | A condition characterized by breathing interruptions during sleep due to a blocked airway, resulting in poor sleep quality and daytime fatigue. |
| Insomnia | A sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, leading to poor sleep quality and daytime fatigue. |
| Shift Work | Working at different hours of the day or night can disrupt the body’s natural sleep schedule and lead to poor sleep quality. |
It is important to establish a regular sleep-wake cycle and practice good sleep hygiene to reduce the risk of sleep paralysis caused by sleep deprivation and disruptive sleep patterns. This includes going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bed, and creating a comfortable sleep environment. In severe cases, a doctor may prescribe medication or recommend therapies to help regulate sleep patterns and improve sleep quality.
Mental Health and Stress
Mental health and stress are commonly associated with sleep paralysis. People who suffer from mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression are more likely to experience sleep paralysis. Stress is a common trigger for sleep paralysis as it disrupts the sleep cycle and causes an increase in cortisol levels.
| Mental Health | Stress |
| — | — |
| Mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression may increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. | Stress can lead to sleep deprivation and disrupt the sleep cycle, causing an increase in cortisol levels. |
| People who have experienced trauma or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) may also be more susceptible to sleep paralysis. | Studies have shown that individuals who experience high levels of stress in their daily lives are more likely to experience sleep paralysis. |
| Sleep paralysis can be a symptom of panic disorder, a type of anxiety disorder. | Lack of sleep due to work, travel, or other factors can increase stress levels and lead to sleep paralysis. |
| Struggling with insomnia, the inability to fall or stay asleep, can lead to exhaustion and stress, making sleep paralysis more likely to occur. | Techniques such as meditation and relaxation exercises may help reduce stress levels and prevent sleep paralysis from occurring. |
It is essential to identify and manage any underlying mental health or stress-related issues to reduce the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. Seeking treatment from a mental health professional or therapist may help manage symptoms and develop coping strategies. Additionally, practicing good sleep hygiene and implementing stress-reducing techniques may improve overall sleep quality and reduce the risk of sleep paralysis.
Symptoms of Sleep Paralysis
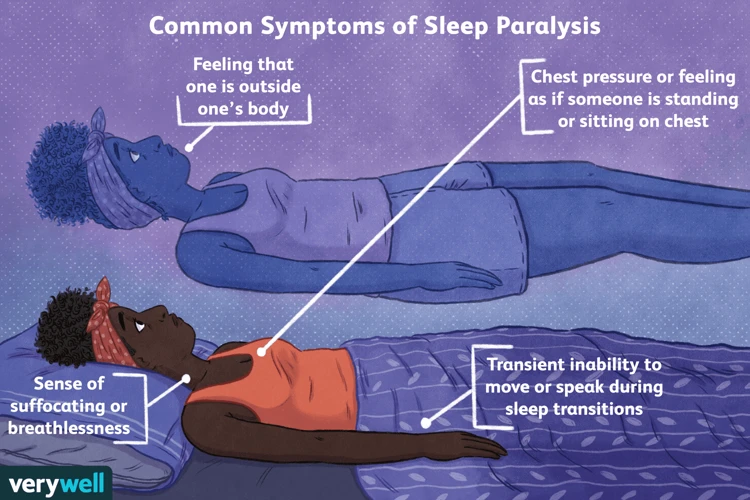
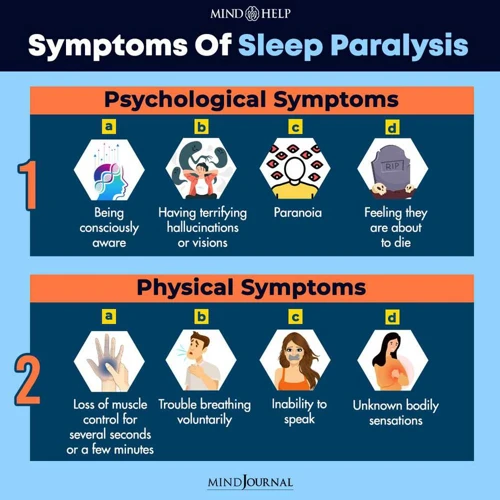
One of the most unsettling features of sleep paralysis is the combination of symptoms experienced by those who suffer from it. These are not limited to physical sensations or mental symptoms – in fact, the most distressing aspect of sleep paralysis is the way that it combines both of these elements into what can be a terrifying experience. In this section, we will explore the different symptoms of sleep paralysis, including the visual and auditory hallucinations, the feeling of physical immobility, and the intense fear that often accompanies an episode.
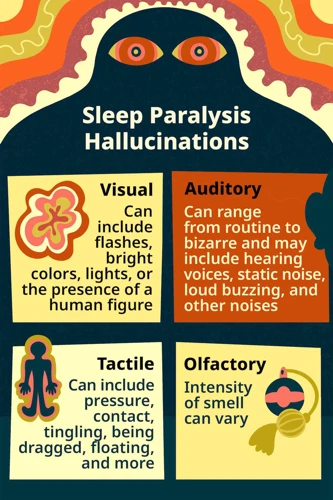
Visual and Auditory Hallucinations
One of the most unsettling symptoms of sleep paralysis is the experience of visual and auditory hallucinations. During an episode of sleep paralysis, the brain remains in a state of sleep even though the person is conscious, leading to vivid and often terrifying hallucinations. These hallucinations can take many forms, including seeing shadowy figures or creatures lurking in the room or hearing mysterious sounds or whispers.
In some cases, these hallucinations can be so intense that they trigger intense feelings of dread, believing that something catastrophic is about to happen. Some people have reported seeing or feeling a presence or entity in the room with them, often described as a sense of impending doom or a malevolent force.
These hallucinations can be particularly distressing for individuals who do not understand what is happening to them, leading to a sense of panic and disorientation. Some individuals have even described feeling as if they were being dragged off the bed or suffocated.
It is important to note that these hallucinations are a normal part of the sleep paralysis experience, and while frightening, they are typically not indicative of a more serious underlying condition. However, if these hallucinations become chronic or if they are accompanied by other symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention.
Here is a table summarizing the visual and auditory hallucinations associated with sleep paralysis:
| Visual Hallucinations | Auditory Hallucinations |
|---|---|
| Shadowy figures or creatures | Mysterious sounds or whispers |
| Sense of presence or entity | Unexplained voices |
| Feeling of impending doom | Unusual noises or music |
| Feeling of being dragged off the bed | Other auditory hallucinations |
Physical Sensation and Immobility
During sleep paralysis, one of the most frightening experiences for many individuals is the physical sensations and immobility that they can experience. This can be an incredibly distressing and frightening experience for those affected by this disorder.
When we sleep, our brain sends signals to our bodies to relax our muscles and cause paralysis. This is so that we don’t act out our dreams in real life and potentially harm ourselves. However, in some cases, the individual may wake up before the paralysis wears off, and they can be left momentarily unable to move or speak. This is known as sleep paralysis.
During this experience, some people may feel a sense of pressure or weight on their chest or body, making them feel as though they are being held down. They may also experience twitching or jerking sensations in their limbs, a sensation of vibration, or numbness and tingling throughout the body. In some cases, the individual may also experience painful sensations or cramps.
The inability to move can be especially frightening, leaving individuals feeling helpless and vulnerable. The inability to speak or call for help can further increase their distress. These physical sensations can be accompanied by visual and auditory hallucinations, which can make the experience even more terrifying.
It’s important to note that while sleep paralysis may be a frightening experience, it is a temporary condition and does not pose any long-term harm to the individual. However, the experience can be quite distressing and may impact an individual’s quality of life. Seeking medical attention and learning coping strategies can help manage the symptoms of sleep paralysis.
The following table summarizes the physical sensations experienced during sleep paralysis:
| Physical Sensations During Sleep Paralysis |
|---|
| Sense of pressure or weight on chest or body |
| Twitching or jerking sensations in the limbs |
| Sensation of vibration |
| Numbness and tingling throughout the body |
| Painful sensations or cramps |
| Inability to move or speak |
Trouble Breathing and Intense Fear
During sleep paralysis, individuals may experience episodes of trouble breathing and intense fear. This can be a terrifying experience, causing feelings of helplessness and panic. The sensation of not being able to move combined with the fear can lead to a racing heartbeat and a sense of suffocation.
In extreme cases, some individuals may hallucinate that they are being choked, adding to the feeling of breathlessness. These symptoms can cause a deep sense of fear and create a vicious cycle where the fear only intensifies the symptoms of sleep paralysis.
It is important to note that while difficulty breathing is a common symptom of sleep paralysis, it is essential to seek medical attention if the symptoms persist or worsen. This can help rule out any underlying medical conditions causing breathing difficulties.
Table: Common Symptoms of Sleep Paralysis
| Visual and Auditory Hallucinations | Physical Sensation and Immobility | Trouble Breathing and Intense Fear |
|---|---|---|
| Seeing or hearing things that aren’t there | Feeling paralyzed or unable to move | Sensation of suffocation or choking |
| Feeling a presence in the room | Feeling pressure or weight on the chest | Feelings of fear, anxiety, or panic |
| Seeing shadowy figures or monsters | Feeling as if floating, flying, or falling | Racing heartbeat |
It is important for individuals who experience sleep paralysis to seek medical attention if their symptoms are causing significant distress or interfering with their ability to sleep. There are several treatment options available that can help manage the symptoms of sleep paralysis and improve overall sleep quality.
Diagnosing Sleep Paralysis
For individuals experiencing sleep paralysis, receiving an accurate diagnosis is crucial in finding effective treatment. Identifying the root cause of this disorder can be complex, as it may involve multiple factors ranging from medical conditions to sleep patterns. A comprehensive medical assessment and sleep study are necessary to diagnose sleep paralysis. Additionally, understanding other sleep-related disorders, such as REM sleep behavior disorder, can aid in the accurate diagnosis of sleep paralysis. Let’s delve into the various methods of diagnosing and understanding sleep paralysis in greater detail.
Medical Assessments and Sleep Studies
In order to properly diagnose sleep paralysis, medical assessments and sleep studies may be necessary. This can involve a range of tests to rule out any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to the symptoms.
Evaluation by a healthcare provider:
A healthcare provider may conduct a thorough medical exam to evaluate the individual’s overall health, sleep patterns, and any potential risk factors related to sleep paralysis. They may also ask about medication use, alcohol consumption, and any psychosocial stresses.
Sleep studies:
Sleep studies, also known as polysomnography, can help monitor an individual’s brain waves, heart rate, muscle activity, and eye movements during sleep. This can help identify patterns of sleep paralysis and other sleep-related disorders. Additionally, sleep studies can identify any potential underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to the symptoms.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI):
MRI scans can be used to evaluate the brain and identify any potential neurological conditions that may be contributing to sleep paralysis.
Electroencephalogram (EEG):
An EEG scan can evaluate an individual’s brain activity during sleep and help identify any potential neurological conditions that may be contributing to sleep paralysis.
It is important to note that while medical assessments and sleep studies can help diagnose sleep paralysis, there is no cure for the condition. Treatment options focus on managing symptoms and improving overall sleep health.
Understanding REM Sleep Behavior Disorder
During REM sleep, the body is usually in a state of paralysis to prevent individuals from acting out their dreams. However, individuals with REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD) experience a loss of this paralysis and may physically act out their dreams. This disorder can be a potential precursor to more serious neurological conditions such as Parkinson’s disease.
Symptoms of RBD include:
- Violent movements during sleep
- Shouting, screaming, or talking during sleep
- Kicking, punching, or flailing arms and legs
- Experiencing vivid and intense dreams
Causes of RBD can include:
- Brain injuries or disorders such as Parkinson’s disease
- Use of certain medications or substances
- Hereditary factors
Treatment for RBD may include:
- Medications such as melatonin or clonazepam to reduce symptoms
- Modifying the sleeping environment to reduce chances of injury
- Seeking treatment for underlying neurological conditions
It is important to note that not everyone who experiences RBD will necessarily go on to develop more serious neurological conditions. However, individuals who suspect they may be experiencing symptoms of RBD should seek medical attention to rule out any underlying conditions and prevent self-injury during the night.
Treating Sleep Paralysis
For those who suffer from sleep paralysis, finding ways to manage and alleviate their symptoms is crucial. While there’s no one-size-fits-all approach to treating sleep paralysis, there are a variety of strategies and techniques that may offer relief. From lifestyle changes to medications and therapies, there are many options available to those looking for help. In this section of the article, we’ll explore some of the most effective methods for treating sleep paralysis and how they can be used to improve sleep quality and reduce the frequency of episodes.
Lifestyle Changes and Good Sleep Hygiene
Lifestyle Changes and Good Sleep Hygiene
Incorporating certain lifestyle changes and adopting good sleep practices can significantly help in managing sleep paralysis. Some of the strategies include:
- Establishing a Sleep Routine: Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends, can help regulate the sleep-wake cycle, allowing the body to get adequate rest and reducing the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
- Improving Sleeping Environment: Ensuring the sleeping environment is conducive to sleep by keeping the room dark, quiet, and cool can promote better sleep quality.
- Reducing Stimulant Intake: Limiting the consumption of caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol, especially before bedtime, can improve sleep quality and reduce the likelihood of sleep paralysis.
- Reducing Screen Time: Avoiding the use of electronic devices before bedtime, as they emit blue light that can affect the circadian rhythm, can help improve sleep quality and reduce the chances of experiencing sleep paralysis.
- Exercise: Incorporating a regular exercise routine can promote better sleep quality and reduce stress levels, which can contribute to sleep paralysis.
Adopting these lifestyle changes and good sleep practices can improve sleep quality, reduce stress levels, and decrease the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
Medications and Therapies
When it comes to treating sleep paralysis, various medications and therapies can be used. Below is a table that outlines some of the most common medications and therapies that have been used to manage this condition.
| Medications | Therapies |
|---|---|
| Antidepressants: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are often prescribed to regulate serotonin levels and improve sleep quality. | Sleep hygiene: Basic sleep hygiene practices like sticking to a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, avoiding caffeine and nicotine, and practicing relaxation techniques can help improve sleep quality and prevent sleep paralysis episodes. |
| Anxiolytics: Anti-anxiety medications like benzodiazepines may be prescribed to help reduce anxiety and improve sleep quality. | Cognitive-behavioral therapy: This type of therapy involves working with a mental health professional to identify and address negative thought patterns and behaviors that may contribute to sleep paralysis. It can be helpful for managing anxiety and improving sleep quality. |
| Stimulants: In some cases, stimulant medications like modafinil may be prescribed to help improve wakefulness and reduce daytime sleepiness. | Lucid dreaming: This technique involves training the mind to become more aware during dream states and can help individuals develop control over their dreams and reduce the occurrence of sleep paralysis. |
| Muscle relaxants: These medications can be helpful for relieving muscle tension and reducing the likelihood of experiencing a sleep paralysis episode. | Yoga and meditation: These practices can help promote relaxation and reduce anxiety, which can contribute to better sleep quality and fewer episodes of sleep paralysis. |
It’s worth noting that not all treatments work for everyone, and treatment may involve a combination of medications and therapies tailored to an individual’s specific case. It’s important to work with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action for managing sleep paralysis.
Alternative and Complementary Techniques
Individuals who experience sleep paralysis can benefit from alternative and complementary techniques as an adjunct to medical treatment. These techniques have shown promising results in reducing the frequency and intensity of sleep paralysis episodes.
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Meditation | Meditation is a practice that helps individuals focus their attention and eliminate distracting thoughts. It has been found to be effective in reducing stress levels that can contribute to the occurrence of sleep paralysis. |
| Yoga | Yoga combines controlled breathing, meditation, and physical postures to improve overall well-being. It has been found to be effective in reducing anxiety, stress, and depression that can contribute to sleep paralysis. |
| Acupuncture | Acupuncture is an alternative medicine practice that involves the insertion of fine needles into specific points of the body to stimulate energy flow. It has been found to be effective in reducing the frequency and intensity of sleep paralysis episodes. |
| Aromatherapy | Aromatherapy involves the use of essential oils to promote relaxation and reduce stress levels. It has been found to be effective in reducing the occurrence of sleep paralysis episodes. |
| Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) | MBSR is a program that combines meditation, yoga, and mindfulness to reduce stress and improve mental well-being. It has been found to be effective in reducing the frequency and intensity of sleep paralysis episodes. |
It is important to note that alternative and complementary techniques should be used in conjunction with medical treatment and should not replace it. It is recommended that individuals consult with a healthcare provider before starting any alternative or complementary technique to ensure their safety and efficacy.
After experiencing sleep paralysis, individuals may feel apprehensive about sleeping and may develop anxiety, further disrupting their sleep patterns. It’s essential to manage sleep paralysis and related disorders effectively to prevent further complications. There are various coping strategies and support networks that can empower individuals to overcome this sleep disorder. In this section, we will explore different techniques that can help individuals manage sleep paralysis and any related disorders that may arise. So, let’s dig deep into these methods and understand how they can help you alleviate sleep-related issues.
Coping Strategies and Support Network
Coping with sleep paralysis can be challenging, but having a support network and utilizing coping strategies can ease the experience. Here are some coping strategies and ways to build a support network:
- Seeking professional support: It can be helpful to seek support from a mental health professional or sleep specialist who can guide you through coping with sleep paralysis and any underlying mental health concerns.
- Journaling: Keeping a journal can help you process your thoughts and emotions surrounding episodes of sleep paralysis. It can also help you identify any triggers or patterns that may contribute to the episodes.
- Practicing relaxation techniques: Engaging in relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or practicing yoga or meditation, can help decrease stress and anxiety that may contribute to sleep paralysis episodes.
- Establishing a regular sleep routine: Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule can help regulate your sleep cycle and reduce the likelihood of sleep paralysis episodes.
- Creating a comfortable sleep environment: Keeping your bedroom cool, dark, and noise-free can promote a restful sleep environment and reduce the occurrence of sleep paralysis.
- Talking to others: Sharing your experiences with trusted friends or family members can help you feel less isolated and provide a sense of comfort and support.
- Joining a support group: Connecting with others who have experienced sleep paralysis can be beneficial in providing a supportive environment to share experiences and coping strategies.
Remember, coping with sleep paralysis can be an ongoing process, but there are numerous strategies and resources available to help manage the experience.
There are several steps that can be taken to prevent or reduce the likelihood of developing sleep-related disorders, including Sleep Paralysis. Here are some tips for maintaining a healthy sleep routine:
- Establish Regular Sleeping Habits: We should try to stick to a consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends or days off. This helps our body to establish a natural sleep cycle, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up at the same time each day.
- Create a Relaxing Sleep Environment: Our bedroom should be quiet, cool, and dark. We may choose to use curtains, eye masks, earplugs, or a sound machine to create a peaceful atmosphere. Also, we should have a comfortable mattress and pillows that support our sleeping position.
- Avoid Stimulants: It’s a good idea to avoid caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol before bed. These substances can disrupt our sleep, making it harder to fall asleep or stay asleep.
- Avoid Large Meals Before Bed: Eating a large meal before bedtime can lead to discomfort and interfere with our sleep. We should try to eat our last meal of the day at least two to three hours before bedtime.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity can help us to fall asleep faster and stay asleep longer. However, it’s important to finish exercising at least two to three hours before bedtime to give our body time to relax.
- Manage Stress: Stress and anxiety can interfere with our sleep. It’s important to find ways to manage stress, such as deep breathing, meditation, or exercise. Also, we should try to avoid activities that can cause stress right before bed.
- Avoid Using Electronic Devices in Bed: The blue light emitted by electronic devices such as phones, tablets, or laptops can interfere with our body’s natural sleep cycle. It’s best to avoid using these devices in bed, or at least to use a blue light filter to reduce the impact.
By following these tips, we can create a healthy sleep routine that helps us to prevent sleep-related disorders such as Sleep Paralysis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sleep paralysis can be a frightening experience for those who suffer from it. While the exact causes of sleep paralysis are not fully understood, it is clear that it is linked to various factors, including neurological and physical factors, sleep patterns, and mental health. The symptoms of sleep paralysis can range from hallucinations to physical immobility, and it can be a challenging disorder to diagnose.
However, there is hope for those who suffer from sleep paralysis. Lifestyle changes such as establishing consistent sleep patterns, reducing stress, and practicing good sleep hygiene can be effective in managing sleep paralysis. Additionally, medications and therapies may be helpful in some cases.
It is important to seek support from loved ones and medical professionals if you are experiencing sleep paralysis. Coping strategies and a supportive network can greatly improve one’s ability to manage the disorder. Furthermore, taking steps to prevent sleep-related disorders can reduce the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis in the future.
Overall, with the right treatment and self-care, sleep paralysis can be effectively managed, allowing individuals to get the restorative sleep they need to live a healthy and fulfilling life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is sleep paralysis and why does it occur?
Sleep paralysis is a temporary inability to move or speak that occurs when a person is waking up or falling asleep. It is caused by a disruption in the normal sleep cycle.
What are the neurological factors that can lead to sleep paralysis?
Neurological factors such as narcolepsy, sleep apnea, or REM sleep behavior disorder can increase your risk of experiencing sleep paralysis.
Can sleep deprivation and disrupted sleep patterns cause sleep paralysis?
Yes, sleep deprivation and irregular sleep schedules can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
Yes, stress and mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression can increase the risk of sleep paralysis.
What are the main symptoms of sleep paralysis?
The main symptoms of sleep paralysis include visual and auditory hallucinations, physical sensation and immobility, and intense fear or panic.
How is sleep paralysis diagnosed?
Doctors may perform a medical assessment and sleep studies to diagnose sleep paralysis. They may also look for signs of REM sleep behavior disorder.
What are some treatments for sleep paralysis?
Treatments for sleep paralysis can include lifestyle changes such as exercise and stress reduction, medication, and therapy. Alternative techniques like meditation and relaxation exercises may also be effective.
Can sleep paralysis be managed and prevented?
Yes, there are coping strategies such as creating a support network and managing stress that can help manage sleep paralysis. Preventative measures include practicing good sleep hygiene and avoiding certain foods and substances before bed.
Is sleep paralysis dangerous?
While sleep paralysis can be scary and distressing, it is not physically dangerous.
Can sleep paralysis be linked to other sleep disorders?
Yes, sleep paralysis can be linked to other sleep disorders such as narcolepsy, sleep apnea, and REM sleep behavior disorder.