For centuries, human beings have been fascinated and puzzled by the phenomenon of nightmares. These jarring, vivid dreams can leave us feeling shaken and anxious even after we wake up. While nightmares are a common experience for many people, they can also be incredibly complex and difficult to understand. What causes us to have such disturbing dreams? Are they just random firings of the brain, or are they somehow connected to our deepest fears and anxieties? In this article, we will explore the science and psychology of nightmares and provide tips for understanding and coping with these unsettling experiences.
Contents
- What Are Nightmares?
- The Science of Nightmares
- The Psychology of Nightmares
- How to Deal with Nightmares
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the difference between nightmares and night terrors?
- Are nightmares more common in children or adults?
- Can medications cause nightmares?
- Can nightmares be a symptom of a mental health disorder?
- What is lucid dreaming and can it be used to control nightmares?
- What is sleep paralysis and can it be related to nightmares?
- Can practicing relaxation techniques before bed help prevent nightmares?
- What is the difference between a recurring nightmare and a dream theme?
- Can nightmares have physical effects on the body?
- Should someone see a therapist if they are experiencing frequent nightmares?
- References
What Are Nightmares?

Nightmares are disturbing and frightening dreams that can cause a person to wake up feeling anxious, terrified, and in some cases, physically shaken. People may experience different types of nightmares, but common themes include being chased or attacked, falling from a great height, or facing their deepest fears.
Types of Nightmares: The nightmares can be classified into different types, such as anxiety dreams, lucid nightmares, and PTSD nightmares. Anxiety dreams usually occur due to a person’s everyday life stressors, whereas lucid nightmares involve becoming aware that you are dreaming but being unable to control the dream’s outcome. PTSD nightmares are a symptom of post-traumatic stress disorder and can be triggered by past traumatic events.
Nightmares can occur at any age, but children are particularly susceptible to them. They can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, anxiety, and trauma. Recent research suggests that nightmares may serve as a coping mechanism for our brains, allowing us to process and confront difficult emotions, memories, and experiences.
Nightmares can be a distressing experience, but they are a natural part of the dreaming mind. Learning to understand their underlying causes and how to manage them can help individuals improve their sleep and overall well-being.
Types of Nightmares
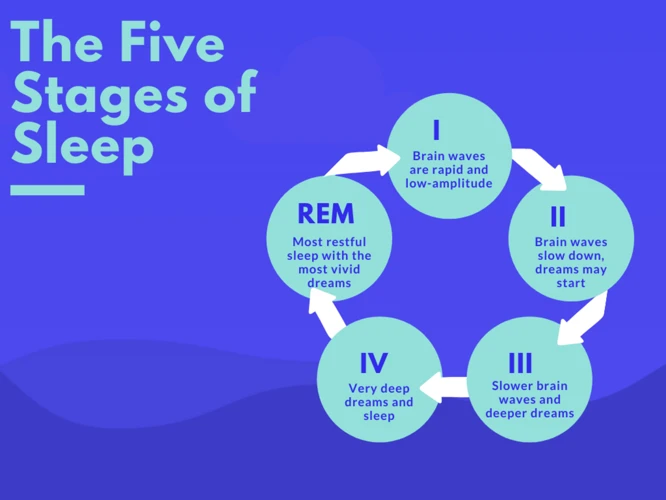
Nightmares are vivid and disturbing dreams that cause feelings of fear, anxiety and terror. They usually occur during the rapid eye movement (REM) phase of sleep and can be quite common in adults and children alike. There are several types of nightmares that people can experience:
Recurrent Nightmares: This type of nightmare is defined as a dream that repeats itself and tends to be very similar each time. This can be quite distressing for people, as it can feel like they are reliving the same terrifying experience over and over again.
Night Terrors: While not technically a nightmare, night terrors are a related sleep disorder that can cause intense fear during sleep. It is often characterized by screaming, sleepwalking, and other physical symptoms.
Lucid Nightmares: These kinds of nightmares are those in which the dreamer is aware that they are dreaming, but they are unable to wake themselves up from the dream. This can be an incredibly scary experience, as it can feel as if the dreamer is trapped in their own terrifying dream.
False Awakening Nightmares: These occur when someone dreams that they have woken up from a nightmare, only to realize that they are still dreaming. This can be a very disorienting experience, as the dreamer can feel like they are unable to escape from the nightmare.
It’s important to note that while nightmares can be very scary, they are a normal part of the human sleep cycle. However, if they occur frequently and begin to affect a person’s quality of life, it may be worth seeking guidance from a mental health professional.
The Science of Nightmares

Nightmares are a common occurrence that affects many individuals. Understanding the science behind nightmares is important to help individuals identify the root cause of their nocturnal terrors. Research has shown that nightmares are often associated with REM (rapid eye movement) sleep, which is the stage in the sleep cycle when dreaming occurs. During REM sleep, the brain is active, and the body is essentially paralyzed to prevent acting out the dreams.
Studies on brain activity during nightmares have revealed that the amygdala, the part of the brain responsible for processing emotions, is more active during nightmares than during normal dreaming. This heightened activity of the amygdala could explain why nightmares feel more intense and emotionally charged than other dreams. Additionally, the prefrontal cortex, the area of the brain responsible for logical reasoning and decision-making, is less active during nightmares. This could explain why individuals often feel helpless during a nightmare and unable to make rational decisions.
Research has also linked nightmares to past trauma and PTSD (post-traumatic stress disorder). Individuals who have experienced a traumatic event are more likely to have nightmares related to the event. The nightmares can be vivid and often recreate the feelings and emotions associated with the trauma. For individuals with PTSD, nightmares can be particularly debilitating, further exacerbating their symptoms.
Stress and anxiety are also major factors that contribute to nightmares. High levels of stress and anxiety can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and increase the frequency of nightmares. These nightmares may not be directly related to a specific event but rather a manifestation of the individual’s underlying stress and anxiety.
Understanding the science behind nightmares is essential in identifying potential remedies and treatment options. By addressing the root cause of the nightmares, individuals can take proactive steps towards preventing them from occurring. Nightmares can disrupt an individual’s sleep and negatively impact their mental health, making it essential to seek help if necessary.
Brain Activity During Nightmares
During nightmares, the brain undergoes intense activity, especially in the amygdala, the hippocampus, and the parietal lobes. This results in a disruption of the usual sleep cycle, with heart rate and breathing accelerating, and the body entering a state of hyperarousal.
Interestingly, during REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep – the stage at which the most vivid dreams occur -, the prefrontal cortex, responsible for logical thinking and decision-making, becomes less active. This may explain why nightmares often feel so real and why the dreamer may not experience the same level of control over the content and progression of the dream as they would during a typical dream.
Some studies have also pointed to an imbalance in certain neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and norepinephrine, as a potential cause of nightmares. This is supported by the observation that some antidepressants that affect these neurotransmitters can lead to a reduction in nightmare frequency.
While the exact mechanisms behind the occurrence of nightmares are not fully understood, research into the brain activity during nightmares has shed some light on the physical changes that accompany these unsettling dreams. This knowledge can help inform therapeutic approaches aimed at alleviating nightmare-related distress.
The Relationship Between Trauma and Nightmares
Nightmares are often associated with trauma, and it is common for individuals who have experienced a traumatic event to have persistent nightmares. Trauma can refer to a wide range of experiences, such as physical or sexual assault, natural disasters, or combat. These experiences can result in a specific type of nightmare known as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) nightmares.
PTSD nightmares are vivid and intense nightmares that often include a re-experiencing of the traumatic event. These nightmares can be so frequent and distressing that they significantly disrupt an individual’s sleep, causing insomnia and other sleep-related issues. PTSD nightmares can lead to a constant state of hyperarousal, making it difficult for individuals to relax and feel safe.
Research has shown that the amygdala, a part of the brain that is responsible for processing emotions, is hyperactive in individuals who have experienced trauma. This hyperactivity can trigger nightmares during sleep, as the brain is unable to process and integrate the traumatic experience into a more manageable memory.
It is important to note that not all individuals who experience trauma will develop PTSD nightmares. Other factors such as age, gender, personality traits, and social support can all play a role in the development of nightmares.
Therapeutic interventions such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) have been shown to be effective in reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares related to trauma. These interventions focus on processing and integrating the traumatic experience, allowing the brain to heal and form more adaptive memories.
Addressing any underlying anxiety or depression related to the trauma can also help to reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Seeking support from loved ones and participating in support groups can provide individuals with a network of understanding individuals who can help them process and heal from their trauma.
Trauma can have a significant impact on an individual’s sleep and mental health. Seeking support and treatment for trauma-related nightmares can lead to improved sleep and overall well-being.
The Role of Anxiety and Stress in Nightmares
It is important to understand that anxiety and stress can be major triggers for nightmares. When individuals experience high levels of stress and anxiety, it can cause them to feel more on edge, agitated, and sensitive to their surroundings. This heightened state of awareness can often manifest itself in the form of nightmares or other vivid dream experiences.
The Impact of Anxiety on Dreams
Anxiety can have a significant impact on the content of dreams, particularly when it comes to nightmares. Individuals who suffer from anxiety disorders such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) may experience more frequent and intense nightmares. These dreams can be particularly disturbing and may be characterized by feelings of terror, panic, and a sense of imminent danger.
The Effect of Stress on Sleep
Stress can also have a negative impact on the quality of sleep, which may contribute to the development of nightmares. When individuals are stressed, their bodies produce higher levels of cortisol, a hormone that can disrupt the normal sleep cycle. This can lead to feelings of restlessness, difficulty falling asleep, and reduced overall sleep quality.
Addressing Anxiety and Stress to Reduce Nightmares
To reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares, it is important to address any underlying anxieties or stressors. This may involve seeking help from a mental health professional to identify and treat any underlying anxiety disorders or other mental health conditions.
Coping Strategies for Nightmares
Additionally, there are a number of coping strategies that individuals can use to help reduce the impact of nightmares. These strategies may include relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation, establishing a calming bedtime routine, and practicing good sleep hygiene, such as avoiding screens before bedtime and keeping a regular sleep schedule.
Conclusion
While nightmares can be distressing, it is important to understand that they are a normal part of the dreaming experience. By addressing any underlying anxieties, reducing stress levels, and practicing good sleep habits, individuals can work to minimize the frequency and intensity of nightmares and improve the overall quality of their sleep.
The Psychology of Nightmares

Nightmares can be a terrifying and distressing experience for those who experience them. They can be so intense that we wake up feeling anxious and scared, unsure of what is real and what is not. But what causes nightmares from a psychological perspective?
One possible explanation for nightmares is that they are a result of the brain’s natural processing of our experiences and emotions. Dreams, including nightmares, are a way for our unconscious mind to process the events of the day, sort through conflicting emotions, and integrate new experiences into our mental and emotional landscape. In a way, nightmares are a natural way for us to deal with the things that we find difficult while we’re awake.
In addition to serving a natural function, nightmares can also be seen as a form of communication, a way for our unconscious mind to tell us something important. This might be a sign that we are anxious or stressed or that there is an unresolved issue from our past that needs attention. Nightmares have also been linked to trauma, particularly post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), as a way for our brain to try and process traumatic events and emotions.
The good news is that there are a variety of defenses that our minds use to protect us from nightmares, whether we realize it or not. Some people are “natural” at protecting themselves from nightmares, and may have fewer nightmares or less intense nightmares in general. Others may use techniques such as visualization or relaxation to try and prevent nightmares from occurring.
Another important aspect of dealing with nightmares from a psychological perspective is dream analysis. Dream analysis can help us to understand the symbols and messages that our unconscious mind is trying to communicate to us through our nightmares. By examining the underlying themes and emotions present in our dreams, we can gain greater insight into our own psyche and work towards resolving any underlying issues.
Dealing with nightmares is not always easy, but it is possible. With the help of preventative techniques and therapies such as dream analysis, we can work towards reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares and achieving a greater sense of emotional well-being.
Defenses Against Nightmares
When it comes to nightmares, there are a few defenses that individuals can utilize to alleviate their frequency and intensity. One possible defense mechanism is distraction. By distracting oneself before sleep, it can help shift their focus away from negative thoughts and emotions, which may trigger nightmares. Some suggested ways to distract oneself include reading a book, listening to calming music or engaging in other relaxing activities.
Another defense mechanism against nightmares is exposure therapy. Exposure therapy involves exposing oneself to their fears, in this case, nightmares, in a controlled environment. Engaging in exposure therapy can help an individual become more desensitized to intense emotions and, thus, lessen the effects of a nightmare.
Additionally, sleep hygiene can also be a helpful defense against nightmares. Practicing good sleep hygiene can help ensure that an individual receives sufficient, uninterrupted rest, which in turn can contribute to a healthy mental state. It includes avoiding caffeine and alcohol, establishing a calming nighttime routine, and sleeping in a comfortable, dark environment.
Lastly, dream analysis can also be a beneficial tool in defending against nightmares. Through analyzing dream content, one can uncover any underlying issues in their subconscious, which may manifest as nightmares. By identifying these issues, individuals can address them and potentially reduce nightmare frequency.
While nightmares can be a challenging and distressing experience, these defense mechanisms can help manage and alleviate their effects. Whether it be through distraction, exposure therapy, sleep hygiene, or dream analysis, individuals can take proactive steps towards protecting their mental wellbeing and experiencing restful sleep.
The Importance of Dream Analysis
Exploring the psychological causes of nightmares can be a complex process, and one of the most important tools in this exploration is dream analysis. Dream analysis is a method of evaluating and interpreting the content of dreams, and can provide valuable insight into the unconscious mind.
Many theories suggest that dreams, including nightmares, contain elements of symbolism and metaphor that reflect aspects of the dreamer’s emotional and psychological state. Dream analysis can help identify these symbols and their meaning, potentially shedding light on repressed or otherwise hidden emotions and desires.
By understanding the underlying emotions and experiences that drive nightmares, individuals can work towards addressing the root cause of these disturbances. This can be particularly useful for individuals who experience frequent or severe nightmares.
However, it is important to note that interpreting dreams, including nightmares, is not an exact science. The same symbols or experiences may have vastly different meanings for different individuals. It is also possible for dreams to contain no deeper psychological significance at all.
Despite these limitations, many mental health professionals view dream analysis as a valuable tool for exploring the unconscious mind and working through psychological issues. Common techniques in dream analysis may include keeping a dream journal, discussing the content of the dream with a therapist or loved one, and exploring the emotions or experiences associated with the dream in greater detail.
While dream analysis may not provide all the answers to the psychological causes of nightmares, it can be a valuable tool in the journey towards greater self-awareness and emotional healing.
How to Deal with Nightmares
When it comes to dealing with nightmares, there are various techniques and approaches that can be helpful. These can include both prevention techniques as well as therapeutic techniques.
Nightmare Prevention Techniques: One of the best ways to deal with nightmares is to prevent them from happening in the first place. Some strategies that can be helpful include practicing good sleep hygiene, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine. Avoiding certain foods, such as caffeine or heavy meals, before bed may also be helpful. Avoiding exposure to traumatic or stressful stimuli before bed can help minimize the occurrence of nightmares.
Therapeutic Techniques for Nightmares: For those who suffer from frequent nightmares, therapeutic interventions may be necessary. One approach is cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), which aims to change negative thought patterns and behaviors that might be contributing to the nightmare problem. Imagery rehearsal therapy (IRT) is another technique that can be helpful, where individuals learn to mentally rehearse a new, positive ending to the nightmare. Other therapies that may be effective include exposure therapy, which involves gradual exposure to traumatic stimuli, and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), which uses eye movements to process traumatic experiences.
It’s important to seek professional support if nightmares are interfering with daily life and causing significant distress. Talking to a therapist or counselor can help address underlying issues that may be contributing to the nightmare problem and develop a personalized plan for managing and preventing nightmares.
Nightmare Prevention Techniques
There are several techniques that can help prevent nightmares from occurring, or at least reduce their frequency. One method is maintaining a consistent sleep schedule. This means going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, including on weekends. This can help regulate the body’s sleep-wake cycle and reduce the likelihood of experiencing disruptive dreams.
Another technique is to create a calm and relaxing environment before bedtime. This can include activities such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation exercises such as deep breathing or meditation. It is also helpful to avoid stimulating activities before bed, such as using electronic devices or watching intense or scary movies.
Pay attention to what you eat and drink before bedtime. Eating a heavy meal or consuming caffeine or alcohol before bed has been linked to increased nightmares. On the other hand, consuming foods that contain tryptophan, such as turkey, bananas or milk, may help to promote a peaceful sleep.
It is important to address any underlying mental health issues that may be contributing to the nightmares. Seeking therapy, practicing mindfulness and meditation, and engaging in regular exercise can all help reduce feelings of anxiety and stress, which are common triggers for nightmares.
Lastly, it may be helpful to keep a dream journal to understand any patterns or recurring themes in your dreams. This can offer insight into any underlying emotions or stresses that may be causing the nightmares. By identifying these patterns, you can work towards addressing them and reducing the likelihood of experiencing nightmares in the future.
Therapeutic Techniques for Nightmares
For those experiencing frequent and disruptive nightmares, seeking out therapeutic techniques may be an effective solution. One such technique is cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), a type of talk therapy that focuses on identifying and changing thought patterns and behaviors.
Another approach is imagery rehearsal therapy (IRT), which involves actively rewiring the brain’s neural networks through visualizing and rehearsing new, positive dream scenarios to replace the negative ones. This technique has been found to be particularly effective for those with PTSD-related nightmares.
Medication can also be used to manage nightmares, particularly in cases where they are caused by underlying mental health issues such as depression or anxiety. Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications are commonly prescribed for this purpose.
Mindfulness and relaxation techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can also be effective in reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares. By calming the mind and reducing stress levels, these practices can help to prevent the occurrence of upsetting dreams.
It’s important to note that not all therapeutic techniques will work for everyone, and finding the right approach may take some trial and error. It’s also crucial to work with a qualified therapist who can tailor treatment to individual needs and provide guidance and support throughout the process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the psychological causes of nightmares can help individuals to better cope with and potentially overcome their nightmares. Nightmares can occur due to various factors such as trauma, anxiety, and stress. Through the analysis of dreams, individuals can uncover deeper subconscious thoughts and emotions that may be contributing to their nightmares.
It is important to utilize defenses against nightmares such as relaxation techniques and creating a peaceful sleeping environment. Seeking professional help and therapy can also provide individuals with the necessary tools to overcome their nightmares.
While nightmares can be terrifying and disruptive to one’s sleep, they serve a purpose in processing emotions and memories. By recognizing and addressing the psychological causes of nightmares, individuals can develop a greater understanding of their own mental and emotional well-being. It is important to prioritize self-care and seek support when needed in order to promote healthy sleep and overall wellness.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between nightmares and night terrors?
Nightmares are vivid dreams that cause fear, anxiety, and/or sadness, and they often wake the dreamer up. Night terrors, on the other hand, are episodes of intense fear and panic that occur during non-REM sleep, and the individual may not fully wake up during the episode.
Are nightmares more common in children or adults?
Nightmares are more common in children, but adults can also experience them.
Can medications cause nightmares?
Yes, certain medications such as antidepressants, beta blockers, and some blood pressure medications have been known to cause nightmares as a side effect.
Can nightmares be a symptom of a mental health disorder?
Yes, nightmares can be a symptom of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, and anxiety disorders.
What is lucid dreaming and can it be used to control nightmares?
Lucid dreaming is when the dreamer is aware that they are dreaming and can sometimes control the dream. It has been used as a technique to control nightmares, but it may also increase the occurrence of lucid nightmares.
Sleep paralysis is a temporary inability to move or speak while falling asleep or waking up. It can be related to nightmares because some people have reported feeling a sense of danger or a presence in the room during episodes of sleep paralysis.
Can practicing relaxation techniques before bed help prevent nightmares?
Yes, practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga before bed may help prevent nightmares by reducing stress and anxiety.
What is the difference between a recurring nightmare and a dream theme?
A recurring nightmare is a specific dream that repeats itself, whereas a dream theme is a recurring element or topic in multiple dreams.
Can nightmares have physical effects on the body?
Yes, nightmares can cause physical effects such as sweating, rapid heartbeat, and difficulty sleeping.
Should someone see a therapist if they are experiencing frequent nightmares?
It is recommended to see a therapist if nightmares are causing significant distress, impacting daily life, or are related to a mental health disorder.