As we close our eyes and drift off into sleep, our minds can sometimes take us to dark places filled with frightening images and scenarios that leave us feeling disturbed and unsettled. These are nightmares, and while they are a common experience, for some people, they can become a recurring problem that disrupts their sleep and impacts their daily lives. In this article, we will explore the types of nightmare disorders and their symptoms. From sleep paralysis to PTSD-related nightmares, we’ll examine what causes these disorders, the risk factors involved, and the different treatment options available for those who suffer from them. Whether you are someone struggling with recurrent nightmares or just curious to learn more, this article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of this perplexing and often misunderstood phenomenon.
Contents
- The Basics of Nightmare Disorders
- The Different Types of Nightmare Disorders and Their Symptoms
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Nightmare Disorders
- Preventing Nightmare Disorders
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the difference between a nightmare and a night terror?
- Can anyone experience nightmare disorders?
- How do I know if I have a nightmare disorder?
- Can medications cause nightmare disorders?
- What is REM sleep behavior disorder?
- How are nightmare disorders diagnosed?
- What are the treatment options for nightmare disorders?
- Can I prevent nightmare disorders?
- What should I do if I experience a night terror?
- Is it normal to have nightmares after a traumatic event?
- References
The Basics of Nightmare Disorders

For some people, sleep is not always a peaceful and restful experience. Those who suffer from nightmare disorders know all too well the distressing effects that come with these disruptive sleep disturbances. It can be a perplexing experience to wake up feeling frightened, confused, or anxious after a nightmare. Understanding the basics of nightmare disorders is important for recognizing and treating these conditions. In this section, we will explore the definition, causes, risk factors, and signs of when to seek medical help for nightmare disorders.
Defining Nightmare Disorder
Nightmare disorder is a type of sleep disorder characterized by frequent and persistent nightmares that interfere with the individual’s ability to sleep, resulting in significant distress and impairment in social and occupational functioning. According to the DSM-5, which is the diagnostic manual used by mental health professionals, nightmare disorder is classified as a REM sleep disorder.
The following table summarizes the defining features of nightmare disorder:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Recurrent nightmares | The individual experiences frequent and persistent nightmares that cause significant distress and interfere with their ability to sleep. |
| Awareness of the dream | The individual is able to recall the content of the nightmare upon awakening and is aware that it was a dream. |
| Disturbances in sleep | The nightmares disrupt the individual’s sleep, causing difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings during the night, or difficulty falling back asleep after waking up from a nightmare. |
| Impairment in functioning | The nightmares cause significant distress and impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. |
| Not attributable to another condition | The nightmares are not caused by another medical or mental health condition, medication, or substance use. |
It is important to note that not all unpleasant dreams or nightmares meet the criteria for nightmare disorder. The occasional nightmare is a normal part of the sleep experience and does not necessarily indicate a sleep disorder. However, if the nightmares become frequent, persistent, and interfere with daily functioning, it may be indicative of nightmare disorder and warrant evaluation by a healthcare professional.
What Causes Nightmare Disorders?
There is no definitive answer as to what causes nightmare disorders. However, researchers have identified several possible factors that contribute to the development of these conditions. Here are some possible factors:
| Factors | Explanation |
| Stress and Trauma | Experiencing stressful life events or trauma can trigger nightmares. Emotional upheavals like the death of a loved one, divorce or separation, accidents, and other distressing events can lead to anxiety and nightmares. |
| Fear | Fear and anxiety can lead to nightmares. Phobias, panic attacks, and other mental health problems can cause night terrors or bad dreams. |
| Medications | Certain medications can cause nightmares as a side effect. Some examples are antidepressants, beta-blockers, antipsychotics, and narcotics. People who stop taking medication may also experience drug withdrawal nightmares. |
| Genetics | Research suggests that some people may be more prone to nightmares due to a genetic predisposition. |
| Substance Use | Alcohol, nicotine, and drug use can interfere with the sleep cycle and increase the likelihood of nightmares. Heavy users of caffeine or alcohol may also experience nightmares. |
| Sleep Deprivation | A lack of sleep or inadequate rest can cause nightmares. |
It is worth noting that some nightmare disorders may have more than one cause, and some causes may be less understood than others. When trying to determine the root cause of a nightmare disorder, it is crucial to seek the help of a qualified healthcare professional.
What Are the Risk Factors for Nightmare Disorders?
Nightmare disorders are a type of sleep disorder that can be caused by various factors. There are certain risk factors that can increase the likelihood of someone experiencing nightmares, including:
- Stress and anxiety: Individuals who experience high levels of stress and anxiety are more likely to have nightmares. The more stress someone is experiencing, the more vivid and intense their nightmares may be.
- Trauma: Those who have experienced trauma, such as physical or sexual abuse, are at an increased risk for recurring nightmares. Traumatic events can have a lasting impact on an individual’s mental and emotional well-being, leading to nightmare disorders.
- Medications: Certain medications have been known to cause nightmares as a side effect. These may include antidepressants, antipsychotics, and blood pressure medications.
- Substance abuse: Individuals who abuse drugs or alcohol are more likely to experience nightmares. Substance abuse can disrupt the brain’s normal sleep cycles and lead to vivid and often disturbing dreams.
- Family history: Nightmare disorders can be hereditary. Individuals who have a family history of nightmare disorders or other sleep disorders may be more likely to experience them themselves.
- Other sleep disorders: People who suffer from other sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome, may be at an increased risk for nightmare disorders. These disorders can disrupt normal sleep patterns and lead to nightmares.
While these risk factors may increase the possibility of experiencing nightmares, it is important to note that not everyone who experiences them has a nightmare disorder. If someone is experiencing regular nightmares that are interfering with their daily life, it is important to seek the help of a medical professional.
When to See a Doctor?
If you experience frequent nightmares, it’s essential to know when to seek medical attention. Here are some signs that indicate the need to see a doctor:
- Disturbance in daily life: When nightmares start affecting your daily life and productivity, it’s time to take it seriously. If you constantly feel fatigued, anxious, or have trouble concentrating during the day, it might be because of nightmares.
- No relief: If you’ve tried self-help techniques like relaxation exercises, maintaining a sleep schedule, and avoiding triggers, yet nightmares persist, it’s time to get professional help.
- Triggered by medication: Certain medications can induce nightmares as a side effect. If you notice an increase in the frequency and intensity of nightmares after starting a new medication, consult your doctor.
- Symptoms of other disorders: Nightmares are often linked with other mental health disorders like anxiety, depression, and PTSD. If you have symptoms of these conditions along with frequent nightmares, it’s crucial to see a doctor.
- Nightmares after trauma: If you’ve experienced a traumatic event and have been having frequent nightmares related to it, it’s a sign of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It’s essential to seek medical help to address the underlying condition.
Remember, nightmares are not just ‘bad dreams.’ They can have a significant impact on your overall well-being and mental health. Seeking professional help can give you the support you need to overcome them.
The Different Types of Nightmare Disorders and Their Symptoms
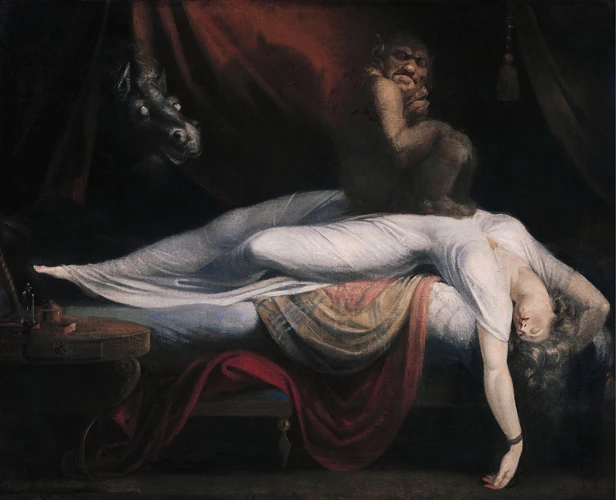

As we delve deeper into the realm of nightmare disorders, we come across various types of these disturbing experiences that can leave a person fearing sleep. From sleep paralysis to post-traumatic stress disorder-related nightmares, each type carries its own set of unique symptoms that can be overwhelming. It’s important to understand the differences between these types of nightmare disorders in order to accurately identify and address them. Let’s explore these different types and their distinctive symptoms in detail.
Nightmare Disorder
Nightmare disorder is a type of sleep disorder that causes recurrent nightmares that interfere with the person’s ability to fall asleep or stay asleep. Some of the key symptoms of nightmare disorder include:
- Recurrent nightmares: The person experiences frequent, disturbing dreams that involve threats to their safety, survival, or well-being. The content of these dreams can vary widely, but they often involve being chased, attacked, or experiencing some kind of trauma.
- Intense fear or anxiety: People with nightmare disorder often wake up feeling extremely frightened or anxious because of the content of their dreams. This fear can be difficult to shake and can interfere with their ability to fall back to sleep.
- Difficulty sleeping: Because the nightmares are so disturbing, people with nightmare disorder may find that they have trouble falling asleep or staying asleep. They may also wake up frequently during the night.
Nightmare disorder can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, anxiety, trauma, and other psychological issues. In some cases, medications or substance abuse can also contribute to the development of nightmare disorder.
Treatment for nightmare disorder typically involves a combination of therapy and medication. Psychotherapy can help people address the underlying psychological issues that are contributing to their nightmares, while medication can help improve sleep and reduce the frequency and intensity of the nightmares themselves.
If you are experiencing recurrent nightmares that are interfering with your ability to sleep or function during the day, it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider or a mental health professional. They can help you determine the underlying cause of your nightmares and develop an effective treatment plan.
Sleep Paralysis
Sleep paralysis is a type of nightmare disorder that is characterized by a feeling of paralysis or inability to move during the transition between sleep and wakefulness. This experience can be terrifying, and may be accompanied by hallucinations or a feeling of presence in the room.
The following table provides a summary of the symptoms of sleep paralysis:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Paralysis | A feeling of being unable to move or speak, typically lasting for a few seconds to a few minutes. |
| Hallucinations | Visual, auditory, or sensory experiences that are not real, such as the feeling of a presence in the room or seeing shadowy figures. |
| Feelings of Anxiety or Fear | A sense of impending doom or terror that can accompany the paralysis and hallucinations. |
| Difficulty Breathing | Some people may feel as though they are having difficulty breathing during an episode of sleep paralysis, which can heighten feelings of panic and anxiety. |
| Sleep Disturbances | Sleep paralysis is often associated with disrupted sleep patterns, and can be more common in people who have existing sleep disorders such as narcolepsy. |
There are several factors that can contribute to sleep paralysis, including sleep deprivation, irregular sleep patterns, certain medications or substances, and underlying mental health conditions. Treatment for sleep paralysis may include improving sleep hygiene, addressing underlying sleep disorders, and in some cases, medication or therapy for anxiety or depression. It is important to speak with a healthcare provider if you are experiencing sleep paralysis or other types of nightmare disorders, as they can help identify underlying causes and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Night Terrors
Night terrors, also known as sleep terrors, are a type of parasomnia disorder that usually occur during non-REM sleep in the first few hours of the night. Unlike nightmares, which tend to happen during REM sleep, night terrors typically occur during slow wave sleep (SWS). This type of disorder typically begins in childhood and can persist into adulthood.
People with night terrors are actually asleep during their episodes, but they experience intense fear and an overwhelming sense of danger or panic. They may sit up, scream, or thrash around in bed, causing injury to themselves or those around them. These episodes can last several minutes and often leave the person feeling confused and disoriented upon awakening.
Symptoms of Night Terrors
The symptoms of night terrors include:
- Intense fear or panic
- Screaming or thrashing around in bed
- Inability to wake up or be comforted by others
- Racing heartbeat and rapid breathing
- Dilated pupils and sweating
- Confusion or disorientation upon awakening
- Amnesia for the episode
It is important to note that these symptoms can be quite distressing for both the person experiencing the night terror and their bed partner or family members who witness the episode.
Causes of Night Terrors
The exact cause of night terrors is unknown, but they may be linked to:
- Stress or anxiety
- Fatigue or lack of sleep
- Sleep deprivation or irregular sleep schedules
- Fever or illness
- Medication use, such as sedatives or antidepressants
- Substance abuse, such as alcohol or drugs
While anyone can experience night terrors, they are more common in children and those with a family history of the disorder.
Treatment for Night Terrors
In most cases, night terrors do not require treatment as they tend to resolve on their own. However, if the episodes are frequent or severe, treatment options may include:
- Identifying and addressing any underlying medical or psychological conditions
- Improving sleep hygiene and establishing a regular sleep schedule
- Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation
- Counseling or therapy to address any underlying anxiety or stress
- Medications, such as benzodiazepines or antidepressants, in severe cases
If you or someone you know is experiencing night terrors, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action.
Rapid Eye Movement (REM) Sleep Behavior Disorder
Rapid Eye Movement (REM) Sleep Behavior Disorder (RBD) is a type of nightmare disorder in which a person acts out vivid, often violent dreams during the REM stage of sleep. Unlike other types of nightmare disorders, RBD occurs mostly in older adults and is more common in men than women. According to a study, RBD affects up to 1% of the population.
One of the hallmarks of RBD is the loss of muscle atonia during REM sleep, which is a natural state of paralysis that usually accompanies REM sleep. Without this paralysis, people with RBD can move, speak or even scream while asleep, which can be disturbing to their bed partners.
Risk factors for RBD include age, as most RBD cases occur in people over the age of 50, as well as neurological conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, multiple system atrophy, and Lewy body dementia. The disorder can also be aggravated by the use of certain medications, such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, and anxiolytics.
The symptoms of RBD can be divided into three categories:
| Category | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Vocalizations and movements | Talking, yelling, punching, kicking, leaping out of bed |
| Violence and aggression | Physically attacking bed partners or others in the room |
| Dreams | Vivid, often violent dreams, often involving animals or attackers |
While RBD itself is not life-threatening, the violent movements and vocalizations associated with it can lead to physical injuries or accidents. It can also be a sign of an underlying neurological or psychiatric condition, which is why a proper diagnosis is crucial.
Treatment options for RBD include medication and lifestyle changes. Clonazepam, a medication used to treat anxiety and seizures, has been found to be effective in reducing the frequency and intensity of RBD episodes. Certain lifestyle changes, such as removing tripping hazards from the bedroom and sleeping in a separate bed from a partner can also help prevent injuries.
People with RBD or those who suspect they may have it should consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment options.
For individuals who have experienced traumatic events, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)-related nightmares may occur. These types of nightmares are not exclusive to combat veterans and may occur in individuals who have experienced any form of trauma, such as sexual assault or natural disasters.
Symptoms of PTSD-related nightmares can include vivid and disturbing dreams that evoke the traumatic event, with the individual often waking up in a state of distress. These nightmares may also involve themes of intense fear, helplessness, or horror, and can cause the individual to relive the traumatic experience, leading to feelings of anxiety and depression.
There are a number of ways in which PTSD-related nightmares can be treated. One approach is to use therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which can help the individual process the traumatic event and reduce anxiety and stress associated with the nightmares. Another option may be the use of medication, such as prazosin, which can reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
It is important for individuals who are experiencing PTSD-related nightmares to seek help from a mental health professional, as these nightmares can have a significant impact on daily life, including sleep quality, mood, and overall well-being.
Substance/Medication-Induced Nightmare Disorder
Substance/Medication-Induced Nightmare Disorder is a type of nightmare disorder that occurs as a result of substance abuse or medications. Certain substances, such as alcohol, opioids, and sedatives, can lead to an increase in nightmares during sleep. Medications such as antidepressants and beta-blockers can also cause this disorder.
Symptoms of Substance/Medication-Induced Nightmare Disorder
The symptoms of this disorder are similar to those of other nightmare disorders. People with this disorder will experience vivid and frightening dreams that can cause a great deal of distress. They may also wake up suddenly in the middle of the night and have trouble falling back asleep.
Causes of Substance/Medication-Induced Nightmare Disorder
The use of substances or medications that affect the brain and disrupt the normal sleep cycle can cause this disorder. Alcohol, opioids, benzodiazepines, and sedatives can all interfere with sleep and cause nightmares. Antidepressants, antipsychotics, and other medications can also increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares.
Treatment for Substance/Medication-Induced Nightmare Disorder
The first step in treating this disorder is to stop using the substance or medication that is causing the nightmares. In some cases, this may require a gradual reduction in the dosage of the medication. Therapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy and exposure therapy, can also be effective in reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
Prevention of Substance/Medication-Induced Nightmare Disorder
To prevent this disorder from happening, it is important to use prescription medications only as directed by a healthcare provider. Substance abuse should be avoided, as it can lead to a number of health problems, including nightmare disorders.
It is important to address the underlying cause of this disorder in order to effectively treat it. A healthcare provider can help individuals find the best treatment options for them based on their specific needs and circumstances.
Nightmares Associated with Medical Conditions
Nightmares can also be associated with various medical conditions. Medical nightmares are often caused by the side effects of medications, chronic pain, and neurological disorders. Some of the medical conditions that can cause nightmares are listed in the following table:
| Medical Condition | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Cancer | Nightmares about the cancer diagnosis, treatment, and the fear of death |
| Chronic Pain | Nightmares about the pain, limited mobility, and frustration |
| Epilepsy | Nightmares about seizures or aura sensations |
| Heart Disease | Nightmares about heart attacks, surgeries, and the fear of dying |
| Migraines | Nightmares about intense headaches and associated symptoms such as nausea and vomiting |
| Multiple Sclerosis | Nightmares about physical limitations and loss of function |
| Obstructive Sleep Apnea | Nightmares about suffocation, choking, and difficulty breathing during sleep |
| Parkinson’s Disease | Nightmares about tremors, rigidity, and difficulty moving |
People who suffer from medical nightmares may experience significant anxiety and distress, which can exacerbate their physical symptoms. It is important for individuals with medical conditions to talk to their healthcare provider about their nightmares and any concerns they may have about their treatment or prognosis. A healthcare provider may be able to adjust medications or recommend therapies to help manage the medical-related nightmares.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Nightmare Disorders
When struggling with nightmare disorders, it is crucial to seek proper diagnosis and treatment. Identification of the underlying cause and severity of the disorder is important for determining the most effective treatment plan. Diagnosis of nightmare disorders typically involves a thorough evaluation of an individual’s medical history, sleep patterns, and symptoms. Treatment options can range from medication to therapy and can often produce significant improvements in an individual’s quality of life. In this section, we will explore the process of diagnosis and the various treatment options available to those dealing with nightmare disorders.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of nightmare disorder involves a thorough evaluation of the individual’s medical history, sleep patterns, and symptoms. Doctors may also perform a physical examination and run diagnostic tests to rule out any underlying medical conditions that could be contributing to the night terrors or nightmares.
The DSM-5 criteria for nightmare disorder are as follows:
| Criterion | Description |
|---|---|
| Recurrent nightmares that occur frequently enough to cause distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other areas of functioning | The individual experiences recurrent, disturbing dreams that lead to significant distress and impairment in daily life. |
| The nightmares are not attributable to the physiological effects of any substance or medication | Excluding nightmares that are caused due to substance or medication intake. |
| Coexisting mental disorders and medical conditions do not adequately explain the predominant complaint of the nightmares | Excluding other psychological or medical reasons behind nightmares. |
The individual may also be asked to keep a dream diary to track the frequency and intensity of their nightmares. Doctors may also use polysomnography, a test that records brainwaves, heart rate, and breathing during sleep, to confirm the diagnosis. Additionally, mental health professionals may conduct psychological assessments or screenings to rule out any underlying mental health disorders.
It is important to note that nightmare disorder is a treatable condition, and individuals who experience frequent nightmares should seek medical attention to get proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Treatment Options
When it comes to treating nightmare disorders, there are several options available. The type of treatment chosen will depend on the underlying cause of the disorder and the specific symptoms experienced by the individual. Here are some of the most common treatment options for nightmare disorders:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This type of therapy aims to change negative thought patterns and behaviors that may be contributing to the nightmares. CBT can help individuals learn new coping mechanisms, relaxation techniques, and better sleep habits.
- Medications: There are several medications that can be used to treat nightmare disorders, including antidepressants, antipsychotics, and some blood pressure medications. It is important to note that while medications can be helpful for some individuals, they do come with potential side effects and should only be used under the supervision of a doctor.
- Hypnotherapy: This therapy involves a trained professional guiding the individual into a relaxed state where they can access their subconscious mind. Hypnotherapy can be used to address the root causes of nightmares and to help individuals find new ways to deal with the emotions associated with them.
- Relaxation Techniques: Techniques like deep breathing, yoga, and meditation can help calm the mind and reduce overall stress levels. By making relaxation techniques a regular part of their routine, individuals may be able to improve the quality of their sleep and reduce the occurrence of nightmares.
- Sleep Hygiene: Making changes to one’s sleep environment and habits can also help reduce the occurrence of nightmares. Strategies like keeping the bedroom cool and dark, avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bedtime, and sticking to a regular sleep schedule can all be helpful.
It is important to note that not all treatments will work for everyone. Finding the right approach may take some trial and error, and it may be necessary to work with a healthcare professional to develop an effective treatment plan. Regardless of the chosen treatment approach, it is important for individuals with nightmare disorders to seek help and support in managing their symptoms.
Preventing Nightmare Disorders
One effective way to prevent Nightmare Disorders is by practicing good sleep habits. Establishing a regular sleep schedule and sticking to it can promote better quality sleep and reduce the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. It’s also essential to create a relaxing bedtime routine that helps calm the mind and body before sleeping.
Limiting or avoiding substances such as alcohol, caffeine, and nicotine before bedtime can also impact the occurrence of nightmares. Certain medications can trigger nightmares, so it’s important to consult with a doctor if experiencing medication-induced nightmares.
Another preventative measure is addressing and treating any underlying medical or psychological conditions that may contribute to nightmares. This may involve seeking therapy or medical treatment to manage symptoms and promote better overall health.
Lastly, reducing exposure to stressful or traumatic situations can also help minimize the chance of experiencing nightmares. Engaging in relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can be useful in reducing stress and promoting better sleep.
Taking steps to improve sleep hygiene, avoiding substances that may induce nightmares, addressing underlying medical or psychological conditions, and reducing exposure to stressful situations can all aid in preventing Nightmare Disorders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, living with nightmare disorders can be a challenging and distressing experience. The different types of nightmare disorders can cause a wide range of symptoms such as sleep disturbances, anxiety, and fear. It is essential to understand the causes and risk factors for these disorders, as well as when to seek medical help.
If you or someone you know is suffering from any of these disorders, it is essential to seek professional guidance and explore the available treatment options. Some people may benefit from simple lifestyle changes and relaxation techniques, while others may need more complex interventions such as medications or therapy.
It is also important to take preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of experiencing nightmare disorders. For example, maintaining a regular sleep routine, avoiding stressful situations before bedtime, and minimizing the use of drugs and alcohol can all help to improve sleep quality and reduce the risk of developing these disorders.
Overall, it is crucial to prioritize sleep and mental health, and seek support when needed. With proper diagnosis, treatment, and self-care, it is possible to manage and cope with nightmare disorders, and achieve a better quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a nightmare and a night terror?
A nightmare is a bad dream that causes feelings of fear, anxiety or sadness, and usually wakes up the person. A night terror is a sudden awakening with feelings of intense fear or terror, usually accompanied by physical symptoms like sweating or rapid heartbeat.
Can anyone experience nightmare disorders?
Yes, anyone can experience nightmare disorders, regardless of age or gender.
How do I know if I have a nightmare disorder?
If you experience recurring terrifying nightmares that disrupt your sleep and cause distress or impairment in daily activities, you may have a nightmare disorder.
Can medications cause nightmare disorders?
Yes, certain medications and substances like antidepressants, beta-blockers, and alcohol can cause nightmare disorders.
What is REM sleep behavior disorder?
REM sleep behavior disorder is a type of nightmare disorder where a person physically acts out their dreams, which can be violent or harmful.
How are nightmare disorders diagnosed?
Nightmare disorders are diagnosed through a thorough medical evaluation, including a review of medical history and sleep patterns, as well as a physical exam and potentially a sleep study.
What are the treatment options for nightmare disorders?
Treatment for nightmare disorders can include therapy, medication, or a combination of both. Therapy may include techniques like image rehearsal therapy or exposure therapy, while medication may include antidepressants or anti-anxiety drugs.
Can I prevent nightmare disorders?
While it may not be possible to prevent nightmare disorders entirely, creating a calming bedtime routine and managing stress levels may help reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
What should I do if I experience a night terror?
During a night terror, it is best to remain calm and avoid waking the person if possible. Simply stay close and reassure them until the episode subsides, as night terrors typically only last a few minutes.
Is it normal to have nightmares after a traumatic event?
Yes, it is normal to experience nightmares after a traumatic event, as this is a common symptom of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Seeking help from a mental health professional may be beneficial in managing these nightmares.